Lab 3
Introduction
In Lab 3, we were tasked with utilizing a keypad that is very prone to mechanical debouncing in order to display numbers on a dual seven segment display that shifted from left to right as new inputs were introduced. This builds on concepts that were utilized in Labs 1 and 2.
Design and Testing Methodology
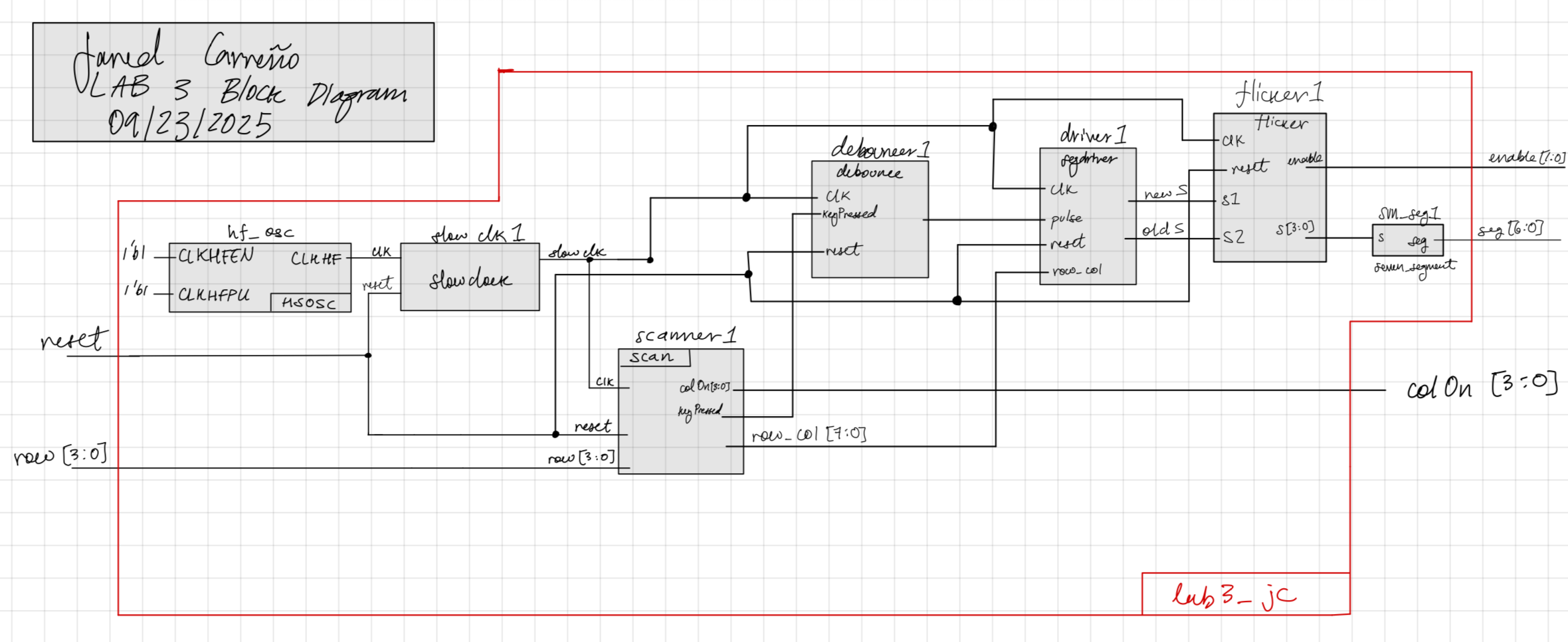
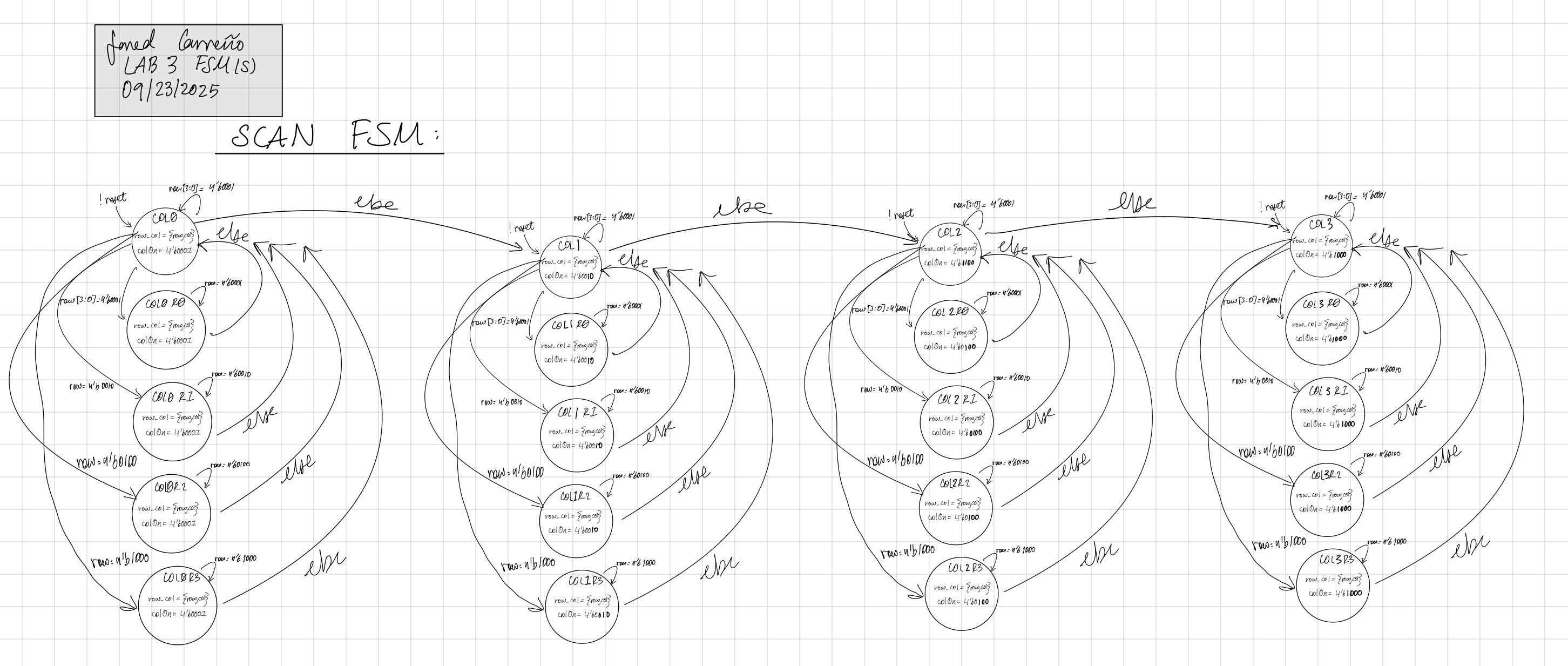
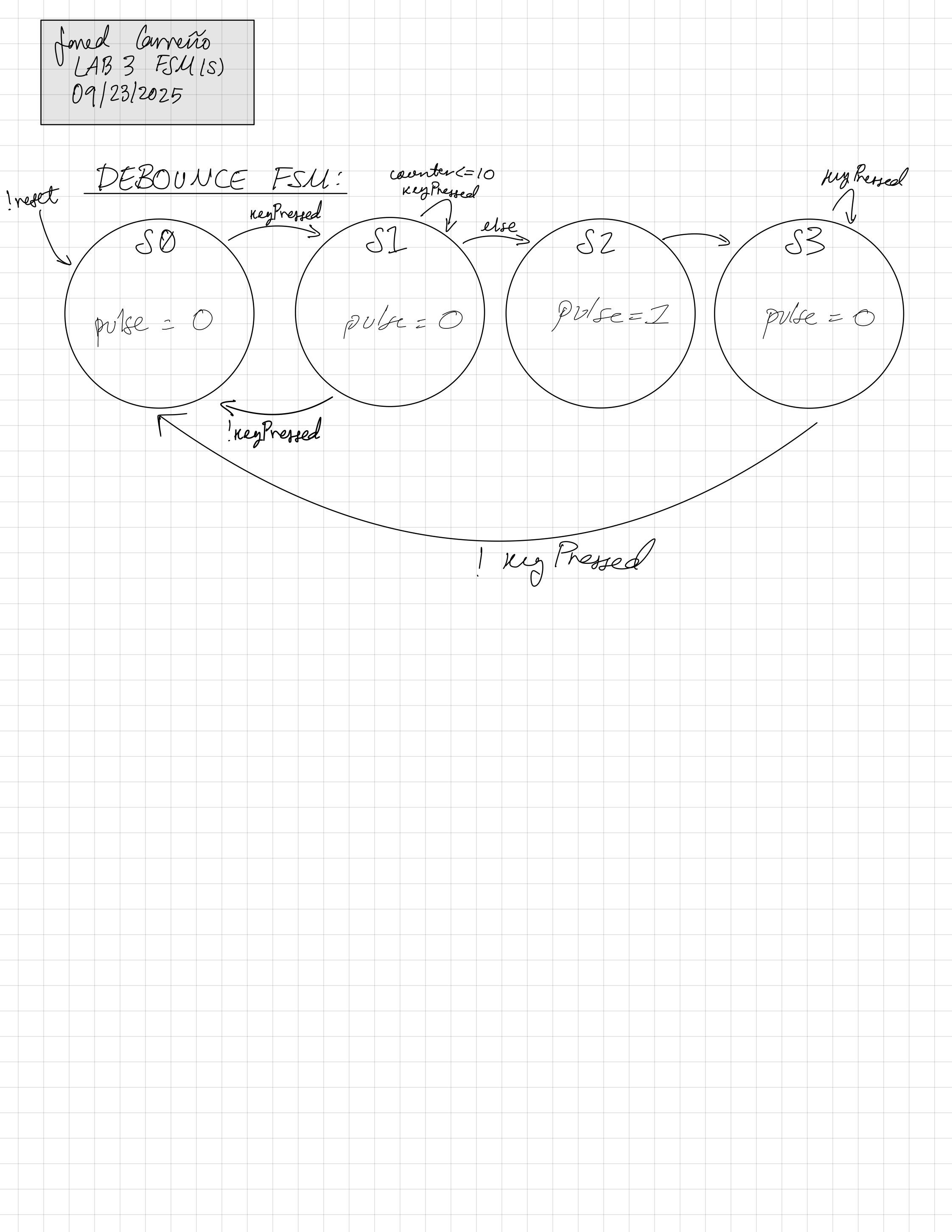
The system was broken down into two FSMs: the scan FSM and debounce FSM:
As shown in Figure 3, the debounce FSM waits for keyPressed to be high, when it detects that it is high, it goes into S1 that enables a counter. Once the counter reaches 50ms and keyPressed is still high, then it moves onto S2 that sets pulse HIGH, indicating that there is a valid key press than can be displayed. If the key is still pressed after it is registered, keyPressed is still HIGH, so the FSM stays in S3 until the key is released, which restarts the FSM waiting for a valid press.
As shown in Figure 2, the scan FSM drives the columns and has a corresponding state for each row and column combination. Using row[3:0], it will jump to the state that corresponds to the column and row, and will set the corresponding column high using colOn[3:0], which cycles through one-hot encodings that enable each column, as the each state outputs row_col = {row, colOn}. The way this is designed ensures that there will be no states where multiple rows are pressed, attempting to limit the possibility of the wrong digits being shown
Technical Documentation:
The Git repository containing the source code of this lab can be found here: Lab 3 Repo.
Block Diagram and FSMs
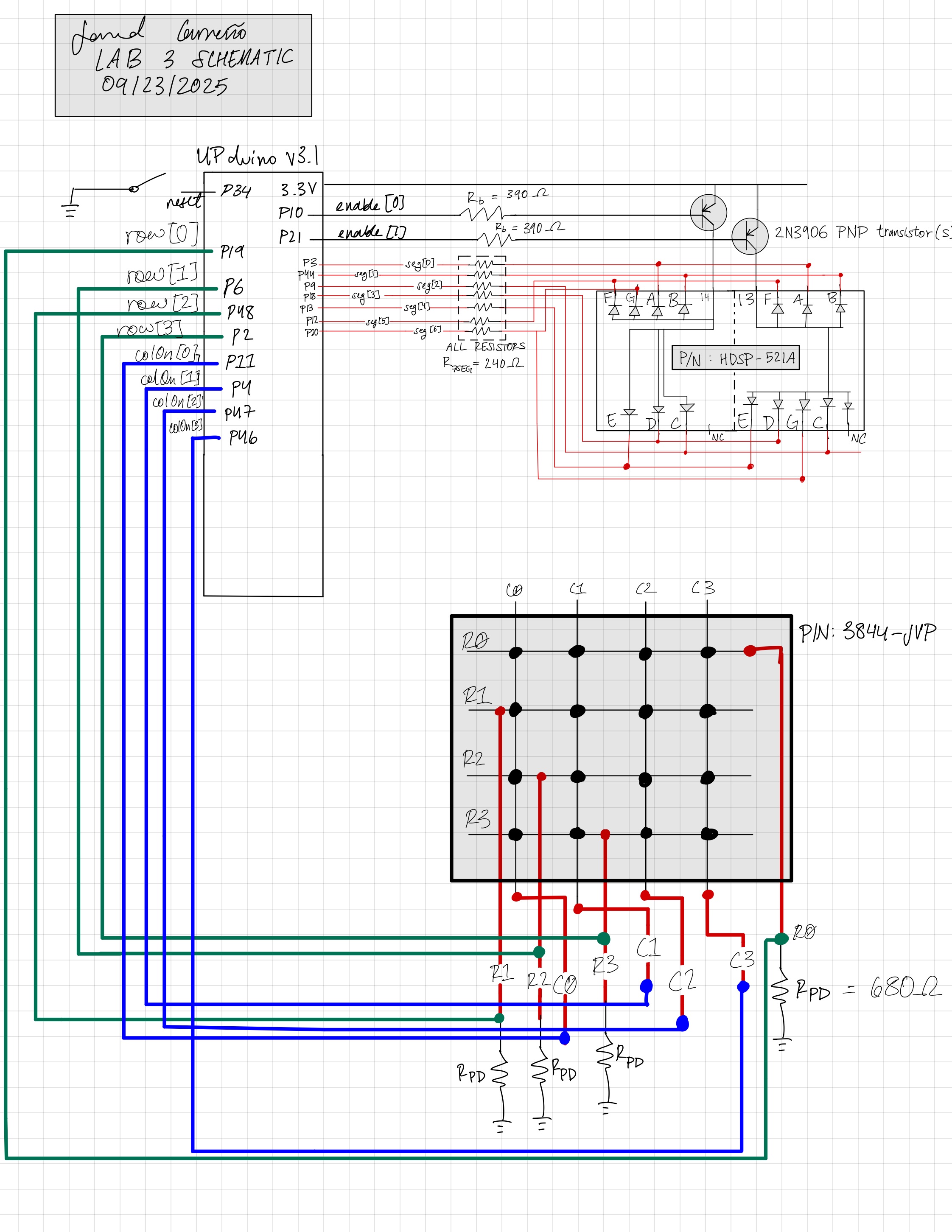
Schematic
Results and Discussion
While there were no testbenches to verify using simulation, the hardware was mostly functional – shifting numbers from right to left (previous to most recent), only registering first key that is pressed, and display the second number held in the same column once the first is released. However, there is a issue when we attempt to switch to a different column from the same row, in which it won’t register the second press if two keys in the same row are pressed at the same time then the first one is released. Overall, it’s a pretty proficient implementation that will be improved on eventually.
Conclusion
My final product was able to successfully work – to an extent, which is further explained in the Results and Discussion section. Overall, this lab took 60+ hours to complete.
AI Prototype Summary
The code produced by the AI contained a lot of syntax errors that did not allow it to synthesize. Notably, it was attempting to find an ‘out’ port, which is not something that our modules are set up to have. There were originally some errors, like the AI creating modules of the same name, but even with some of my intervention the syntax errors were still prominent. The code is shown below:
` module clock_divider( input logic clk, // 20 MHz input clock input logic rst_n, // Active low reset output logic scan_clk // Divided clock (100–200 Hz) ); // Target clock frequency: 100 Hz // Divider for 20 MHz: 20 MHz / 100 Hz = 200,000 logic [18:0] counter; // 19-bit counter for clock division
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
counter <= 0;
scan_clk <= 0;
end else begin
if (counter == 199_999) begin
counter <= 0;
scan_clk <= ~scan_clk; // Toggle scan clock
end else begin
counter <= counter + 1;
end
end
endendmodule
module keypad_scanner1( input logic clk, // Clock input (scan clock) input logic rst_n, // Active low reset input logic [3:0] rows, // Row signals (active low) output logic [3:0] cols, // Column signals (active low) output logic [3:0] key // Output the detected key (hex value) ); // State machine for scanning rows and columns typedef enum logic [1:0] { IDLE = 2’b00, SCAN = 2’b01, DEBOUNCE = 2’b10 } state_t;
state_t state, next_state;
logic [3:0] column_reg, last_cols;
logic [3:0] key_reg, last_key;
logic key_pressed;
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
cols <= 4'b1111; // All columns inactive
key_reg <= 4'b0000;
last_cols <= 4'b1111;
end else begin
state <= next_state;
end
end
// State machine logic
always_ff @(state or column_reg or rows or last_cols) begin
case (state)
IDLE: begin
next_state = SCAN;
cols = 4'b1111; // All columns inactive
end
SCAN: begin
// Cycle through columns, one active at a time
if (column_reg == 4'b1110) column_reg = 4'b1101;
else if (column_reg == 4'b1101) column_reg = 4'b1011;
else if (column_reg == 4'b1011) column_reg = 4'b0111;
else column_reg = 4'b1111;
cols = column_reg; // Set current column
key_pressed = |(rows & ~cols); // Detect key press based on row signals
if (key_pressed) begin
key_reg = rows; // Register key press based on row active
next_state = DEBOUNCE;
end else begin
next_state = SCAN;
end
end
DEBOUNCE: begin
// Debounce the key by ensuring release before registering new key
if (~|(rows & ~cols)) begin // No key pressed
next_state = SCAN;
end else begin
next_state = DEBOUNCE;
end
end
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
// Output the detected key
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
if (key_pressed) key = key_reg;
else key = last_key;
endendmodule
module keypad_one_shot_registration( input logic clk, // Clock input input logic rst_n, // Active low reset input logic [3:0] rows, // Row signals from keypad (active low) output logic new_key, // Single-cycle pulse for new key press output logic [3:0] key_code // Detected key code (hex value) ); // State machine states typedef enum logic [1:0] { IDLE = 2’b00, PRESSED = 2’b01, RELEASED = 2’b10 } state_t;
state_t state, next_state; // Current and next states
logic [3:0] last_key; // Store the last detected key
logic [3:0] current_key; // Store the current key being pressed
// Key detection: any active row means a key is pressed
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
new_key <= 0;
last_key <= 4'b0000;
key_code <= 4'b0000;
end else begin
state <= next_state;
end
end
// Logic for key detection (rows are active low, check if any row is pressed)
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
if (state == IDLE && ~(|rows)) begin
// Detect the key code when a key is pressed (active low rows)
current_key <= ~rows;
end
end
// State transition and new key pulse generation
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
case (state)
IDLE: begin
if (~(|rows)) begin // Detect key press (any active row)
next_state <= PRESSED;
new_key <= 1; // Generate a one-shot pulse
end else begin
next_state <= IDLE;
new_key <= 0; // No new key, reset pulse
end
end
PRESSED: begin
if (~(|rows)) begin // Key is still pressed
next_state <= PRESSED;
new_key <= 0; // No new key until key is released
end else begin
next_state <= RELEASED; // Key released, move to RELEASED state
end
end
RELEASED: begin
if (~(|rows)) begin // Key press has been released
next_state <= IDLE;
key_code <= current_key; // Capture the key code
last_key <= current_key;
end else begin
next_state <= RELEASED;
end
end
default: begin
next_state <= IDLE;
end
endcase
endendmodule
module keypad_scanner2( input logic clk, // Clock input (divided clock) input logic rst_n, // Active low reset input logic [3:0] rows, // Row signals from keypad (active low) output logic [3:0] key_code, // Detected key code (4-bit hex value) output logic key_pressed // Boolean indicating key press status );
// Define FSM states
typedef enum logic [1:0] {
SCAN_IDLE = 2'b00, // Wait for key press
SCAN_COL_0 = 2'b01, // Scan column 0
SCAN_COL_1 = 2'b10, // Scan column 1
SCAN_COL_2 = 2'b11 // Scan column 2
} state_t;
state_t state, next_state; // Current and next states
logic [3:0] col_mask; // Column select mask
logic [3:0] detected_key; // Detected key code (4 bits)
// State machine for scanning columns
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
state <= SCAN_IDLE;
col_mask <= 4'b1111; // All columns inactive initially
end else begin
state <= next_state;
end
end
// Column scanning logic: one column is active (low) at a time
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
case (state)
SCAN_IDLE: begin
col_mask <= 4'b1111; // No column active
end
SCAN_COL_0: begin
col_mask <= 4'b1110; // Only column 0 is active (low)
end
SCAN_COL_1: begin
col_mask <= 4'b1101; // Only column 1 is active (low)
end
SCAN_COL_2: begin
col_mask <= 4'b1011; // Only column 2 is active (low)
end
default: begin
col_mask <= 4'b1111; // Default: no column active
end
endcase
end
// Detect the key code based on the active column and row signals
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
case (state)
SCAN_COL_0: begin
if (~rows[0]) detected_key <= 4'b0001; // Row 0, Column 0
else if (~rows[1]) detected_key <= 4'b0100; // Row 1, Column 0
else if (~rows[2]) detected_key <= 4'b0111; // Row 2, Column 0
else if (~rows[3]) detected_key <= 4'b1000; // Row 3, Column 0
end
SCAN_COL_1: begin
if (~rows[0]) detected_key <= 4'b0010; // Row 0, Column 1
else if (~rows[1]) detected_key <= 4'b0101; // Row 1, Column 1
else if (~rows[2]) detected_key <= 4'b0110; // Row 2, Column 1
else if (~rows[3]) detected_key <= 4'b1001; // Row 3, Column 1
end
SCAN_COL_2: begin
if (~rows[0]) detected_key <= 4'b0011; // Row 0, Column 2
else if (~rows[1]) detected_key <= 4'b0110; // Row 1, Column 2
else if (~rows[2]) detected_key <= 4'b0111; // Row 2, Column 2
else if (~rows[3]) detected_key <= 4'b1011; // Row 3, Column 2
end
default: detected_key <= 4'b0000; // Default: no key detected
endcase
end
// Key press indicator: Any key pressed when one of the rows is active
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
if (~(|rows)) // If any row is active, a key is pressed
key_pressed <= 1'b1;
else
key_pressed <= 1'b0;
end
// Output the detected key code
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
key_code <= detected_key;
end
// State machine transitions: cycle through the columns
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
case (state)
SCAN_IDLE: next_state <= SCAN_COL_0;
SCAN_COL_0: next_state <= SCAN_COL_1;
SCAN_COL_1: next_state <= SCAN_COL_2;
SCAN_COL_2: next_state <= SCAN_IDLE;
default: next_state <= SCAN_IDLE;
endcase
endendmodule
module top_level ( input logic clk, // Clock from internal oscillator input logic rst_n, // Active low reset input logic [3:0] rows, // Row signals from keypad (active low) output logic [6:0] seg_a, // Seven segment display segments for first digit output logic [6:0] seg_b, // Seven segment display segments for second digit output logic an0, // Enable signal for first digit output logic an1 // Enable signal for second digit );
// Signals for keypad scanner and one-shot registration
logic [3:0] key_code; // Detected key code
logic new_key; // New key detected (one-shot signal)
logic key_pressed; // Key pressed indicator
// Signals for last two keys
logic [3:0] most_recent_key; // Most recent key (new key)
logic [3:0] older_key; // Older key (last key)
// Signals for 7-segment display
logic [3:0] display_digit; // Digit to be displayed on the multiplexed display
logic mux_select; // Multiplexer to select which digit to display
// Instantiate the keypad scanner
keypad_scanner2 scanner (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.rows(rows),
.key_code(key_code),
.key_pressed(key_pressed)
);
// Instantiate the keypad one-shot registration module
keypad_one_shot_registration one_shot (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.rows(rows),
.new_key(new_key),
.key_code(key_code)
);
// Process for shifting the last two keys (older <- most recent; most recent <- new)
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
most_recent_key <= 4'b0000;
older_key <= 4'b0000;
end else if (new_key) begin
// Shift the keys when a new key is detected
older_key <= most_recent_key;
most_recent_key <= key_code;
end
end
// Clock divider logic to generate a slower clock for display multiplexing
logic clk_display;
reg [15:0] clk_divider; // Divider for the clock (adjust for desired multiplexing rate)
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
clk_divider <= 16'b0;
clk_display <= 0;
end else begin
// Divide the clock to get a slower rate (e.g., 60 Hz for multiplexing)
if (clk_divider == 16'd49999) begin // Adjust this value for desired rate
clk_divider <= 16'b0;
clk_display <= ~clk_display; // Toggle the display clock
end else begin
clk_divider <= clk_divider + 1'b1;
end
end
end
// Multiplexed display logic: alternate between displaying the two digits
always_ff @(posedge clk_display or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
mux_select <= 0;
display_digit <= 4'b0000;
an0 <= 1;
an1 <= 0;
end else begin
if (mux_select) begin
display_digit <= most_recent_key;
an0 <= 0;
an1 <= 1; // Enable second digit
end else begin
display_digit <= older_key;
an0 <= 1; // Enable first digit
an1 <= 0;
end
mux_select <= ~mux_select; // Toggle between the two digits
end
end
// Instantiate the seven-segment display decoder for both digits
seven_segment seg1(
.in(display_digit),
.out(seg_a)
);
seven_segment seg2(
.in(display_digit),
.out(seg_b)
);endmodule